- AAA - Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
- AC - Alternating Current
- ACL - Access Control List
- ADF - Automatic Document Feeder
- AES - Advanced Encryption Standard
- AP - Access Point
- APFS - Apple File System
- APIPA - Automatic Private Internet Protocol Addressing
- APK - Android Package
- ARM - Advanced RISC [Reduced Instruction Set Computer] Machine
- ARP - Address Resolution Protocol
- ATA - Advanced Technology Attachment
- ATM - Asynchronous Transfer Mode
- ATX - Advanced Technology Extended
- AUP - Acceptable Use Policy
- BIOS - Basic Input/Output System
- BSOD - Blue Screen of Death
- BYOD - Bring Your Own Device
- CAD - Computer-aided Design
- CAPTCHA - Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart
- CD - Compact Disc
- CDFS - Compact Disc File System
- CDMA - Code-Division Multiple Access
- CERT - Computer Emergency Response Team
- CIFS - Common Internet File System
- CMD - Command Prompt
- CMOS - Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor
- CPU - Central Processing Unit
- CRL - Certificate Revocation List
- DC - Direct Current
- DDoS - Distributed Denial of Service
- DDR - Double Data Rate
- DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- DIMM - Dual Inline Memory Module
- DKIM - DomainKeys Identified Mail
- DMA - Direct Memory Access
- DMARC - Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance
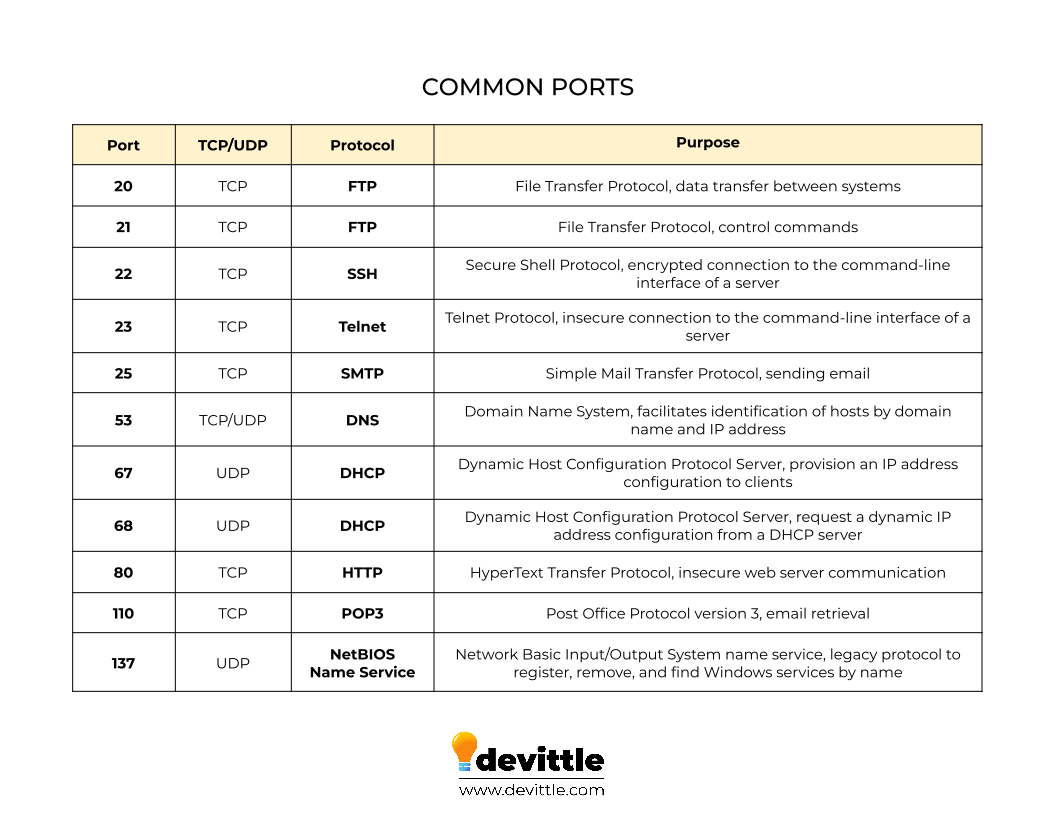
- DNS - Domain Name System
- DoS - Denial of Service
- DRAM - Dynamic Random-Access Memory
- DRM - Digital Rights Management
- DSL - Digital Subscriber Line
- DVI - Digital Visual Interface
- DVI-D - Digital Visual Interface-Digital
- ECC - Error Correcting Code
- EFS - Encrypting File System
- EMI - Electromagnetic Interference
- EOL - End-of-Life
- eSATA - External Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
- ESD - Electrostatic Discharge
- EULA - End-User License Agreement
- exFAT - Extensible File Allocation Table
- ext - Extended File System
- FAT - File Allocation Table
- FAT12 - 12-bit File Allocation Table
- FAT16 - 16-bit File Allocation Table
- FAT32 - 32-bit File Allocation Table
- FSB - Front-Side Bus
- FTP - File Transfer Protocol
- GFS - Grandfather-Father-Son
- GPS - Global Positioning System
- GPT - GUID [Globally Unique Identifier] Partition Table
- GPU - Graphics Processing Unit
- GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
- GUI - Graphical User Interface
- GUID - Globally Unique Identifier
- HAL - Hardware Abstraction Layer
- HAV - Hardware-assisted Virtualization
- HCL - Hardware Compatibility List
- HDCP - High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection
- HDD - Hard Disk Drive
- HDMI - High-Definition Multimedia Interface
- HSM - Hardware Security Module
- HTML - Hypertext Markup Language
- HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol
- HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
- I/O - Input/Output
- IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service
- ICR - Intelligent Character Recognition
- IDE - Integrated Drive Electronics
- IDS - Intrusion Detection System
- IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- IMAP - Internet Mail Access Protocol
- IOPS - Input/Output Operations Per Second
- IoT - Internet of Things
- IP - Internet Protocol
- IPS - Intrusion Prevention System
- IPS - In-plane Switching
- IPSec - Internet Protocol Security
- IR - Infrared
- IrDA - Infrared Data Association
- IRP - Incident Response Plan
- ISO - International Organization for Standardization
- ISP - Internet Service Provider
- ITX - Information Technology eXtended
- KB - Knowledge Base
- KVM - Keyboard-Video-Mouse
- LAN - Local Area Network
- LC - Lucent Connector
- LCD - Liquid Crystal Display
- LDAP - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- LED - Light-emitting Diode
- MAC - Media Access Control/Mandatory Access Control
- MAM - Mobile Application Management
- MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
- MBR - Master Boot Record
- MDM - Mobile Device Management
- MFA - Multifactor Authentication
- MFD - Multifunction Device
- MFP - Multifunction Printer
- MMC - Microsoft Management Console
- MOU - Memorandum of Understanding
- MSDS - Material Safety Data Sheet
- MSRA - Microsoft Remote Assistance
- MX - Mail Exchange
- NAC - Network Access Control
- NAT - Network Address Translation
- NDA - Non-disclosure Agreement
- NetBIOS - Networked Basic Input/Output System
- NetBT - NetBIOS over TCP/IP [Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol]
- NFC - Near-field Communication
- NFS - Network File System
- NIC - Network Interface Card
- NTFS - New Technology File System
- NVMe - Non-volatile Memory Express
- OCR - Optical Character Recognition
- OLED - Organic Light-emitting Diode
- ONT - Optical Network Terminal
- OS - Operating System
- PaaS - Platform as a Service
- PAN - Personal Area Network
- PC - Personal Computer
- PCIe - Peripheral Component Interconnect Express
- PCL - Printer Command Language
- PE - Preinstallation Environment
- PII - Personally Identifiable Information
- PIN - Personal Identification Number
- PKI - Public Key Infrastructure
- PoE - Power over Ethernet
- POP3 - Post Office Protocol 3
- POST - Power-on Self-Test
- PPP - Point-to-Point Protocol
- PRL - Preferred Roaming List
- PSU - Power Supply Unit
- PXE - Preboot Execution Environment
- RADIUS - Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service
- RAID - Redundant Array of Independent (or Inexpensive) Disks
- RAM - Random-access Memory
- RDP - Remote Desktop Protocol
- RF - Radio Frequency
- RFI - Radio-Frequency Interference
- RFID - Radio-Frequency Identification
- RJ11 - Registered Jack Function 11
- RJ45 - Registered Jack Function 45
- RMM - Remote Monitoring and Management
- RTO - Recovery Time Objective
- SaaS - Software as a Service
- SAN - Storage Area Network
- SAS - Serial Attached SCSI [Small Computer System Interface]
- SATA - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
- SC - Subscriber Connector
- SCADA - Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
- SCP - Secure Copy Protection
- SCSI - Small Computer System Interface
- SDN - Software-defined Networking
- SFTP - Secure File Transfer Protocol
- SIM - Subscriber Identity Module
- SIMM - Single Inline Memory Module
- S.M.A.R.T. - Self-monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
- SMB - Server Message Block
- SMS - Short Message Service
- SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol
- SNTP - Simple Network Time Protocol
- SODIMM - Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module
- SOHO - Small Office/Home Office
- SPF - Sender Policy Framework
- SQL - Structured Query Language
- SRAM - Static Random-access Memory
- SSD - Solid-State Drive
- SSH - Secure Shell
- SSID - Service Set Identifier
- SSL - Secure Sockets Layer
- SSO - Single Sign-on
- ST - Straight Tip
- STP - Shielded Twisted Pair
- TACACS - Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System
- TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
- TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
- TFTP - Trivial File Transfer Protocol
- TKIP - Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
- TLS - Transport Layer Security
- TN - Twisted Nematic
- TPM - Trusted Platform Module
- UAC - User Account Control
- UDP - User Datagram Protocol
- UEFI - Unified Extensible Firmware Interface
- UNC - Universal Naming Convention
- UPnP - Universal Plug and Play
- UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply
- USB - Universal Serial Bus
- UTM - Unified Threat Management
- UTP - Unshielded Twisted Pair
- VA - Vertical Alignment
- VDI - Virtual Desktop Infrastructure
- VGA - Video Graphics Array
- VLAN - Virtual LAN [Local Area Network]
- VM - Virtual Machine
- VNC - Virtual Network Computer
- VoIP - Voice over Internet Protocol
- VPN - Virtual Private Network
- VRAM - Video Random-access Memory
- WAN - Wide Area Network
- WEP - Wired Equivalent Privacy
- WISP - Wireless Internet Service Provider
- WLAN - Wireless LAN [Local Area Network]
- WMN - Wireless Mesh Network
- WPA - WiFi Protected Access
- WWAN - Wireless Wide Area Network
- XSS - Cross-site Scripting
💡
Quick Disclaimer: The content on this site is intended to be a helpful tool on your tech learning journey, but in the end, please rely on your own research and good judgement. If you have suggestions, comments, or questions about the content feel free to contact me. Helpful feedback is always welcome and appreciated!
- 802.11 Standards - a set of wireless networking standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for wireless local area networks (LANs) specifying protocols for wireless communication, including Wi-Fi, with variations such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax
- 802.3 Standards - a set of networking standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) specifying the physical and data link layers of the OSI model for wired Ethernet networks, including specifications for hardware and protocols for data transmission
- Adapter Cable - a cable used to connect devices or peripherals with different types of connectors or interfaces, typically having different connectors on each end
- Adapter Card - a hardware component, also known as expansion cards or interface cards, that can be installed in a computer's expansion slot to provide additional functionality or connectivity, and can include network adapters, graphics cards, sound cards, and other specialized hardware
- Analog - common in audio, video, and other natural phenomena, a signal or device that represents information using continuously varying physical quantities, such as voltage or amplitude, as opposed to discrete digital signals that use binary digits (0s and 1s)
- ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) - a standard for computer motherboard and power supply design introduced by Intel
- Audio Port - interface on a computer or audio device used for connecting headphones, microphones, speakers, or other audio equipment
- Backwards-Compatible - the ability of a newer version of a technology, software, or hardware to work seamlessly with older versions, ensuring compatibility and allowing users to use older devices or software with newer ones without issues
- Bandwidth - represents the capacity of the channel to transmit data within a given period of time and refers to the maximum data transfer rate of a network or communication channel, typically measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps)
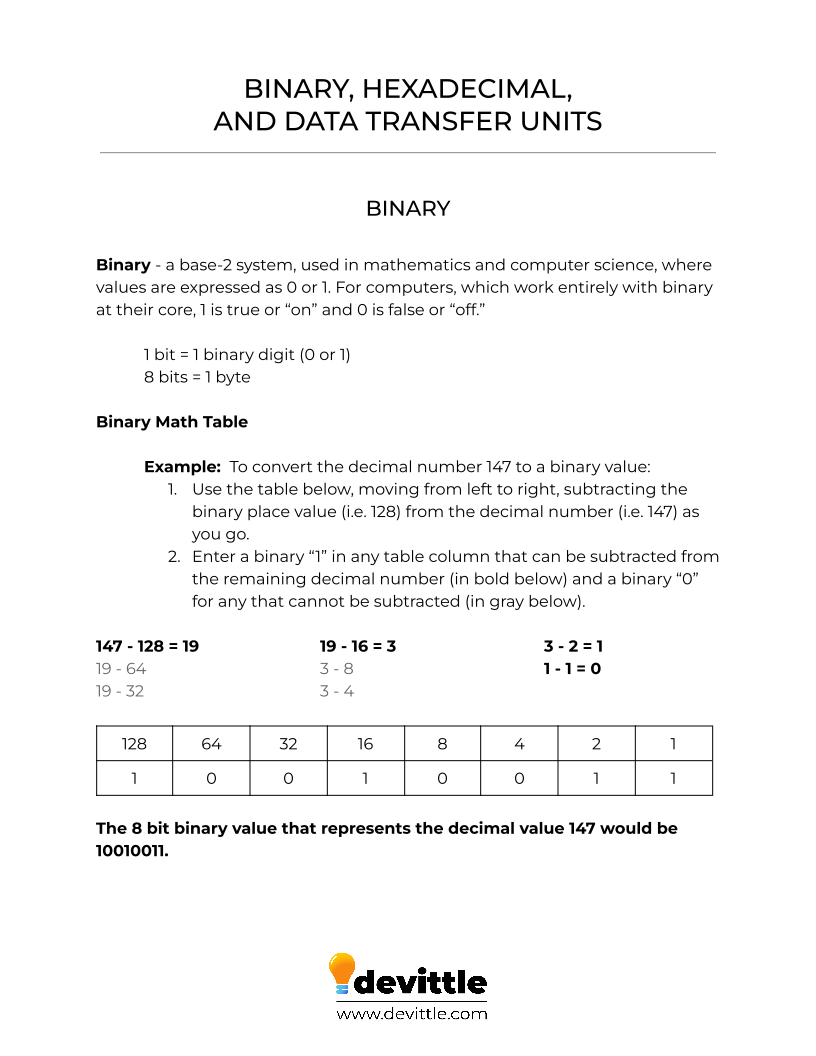
- Binary - a numbering system based on two digits, 0 and 1, used in digital electronics and computing, where each digit is referred to as a bit
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) - firmware embedded in a computer's motherboard that initializes hardware components during the boot process and provides basic input/output services for the operating system
- Blanking Plates - metal or plastic covers used to fill empty expansion card slots or drive bays in a computer case, helping to maintain proper airflow and aesthetics
- Bus - a communication system, consisting of a set of parallel conductors or traces, that transfers data between components inside a computer, between computers, or carry signals between different parts of the computer
- Capacitor - an electronic component that stores electrical energy temporarily and releases it when needed, commonly used for filtering, smoothing, and voltage regulation in electronic circuits
- Capture Card - a device that captures video and audio signals from an external source, such as a gaming console or camera, and converts them into digital signals to be recorded, stored, or streamed via a computer
- Central Processing Unit (CPU) - the primary processing component, or 'brain', of a computer responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and managing data and processes within the computer system
- Chassis Fan - a fan mounted inside the computer case or chassis to provide airflow and dissipate heat generated by internal components, helping to prevent overheating and maintain system stability
- Chipset - a set of integrated circuits on a motherboard or expansion card that manages communication between the processor, memory, peripherals, and other components, facilitating their interaction and operation
- Clock Multipliers - circuitry within a processor or motherboard that increases the speed of the CPU by multiplying the external clock frequency, thereby allowing for faster data processing
- CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) - a type of integrated circuit technology used in modern computer processors and memory modules, known for its low power consumption and high integration density
- Component - individual hardware that make up a computer or electronic device
- Computer - an electronic device capable of receiving, storing, processing, and outputting data, typically operated under the control of programs or instructions
- Connector - a mechanical device used to join electrical circuits or components together, commonly found at the ends of cables, facilitating the transfer of signals, power, or data between them
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) - a display technology used in older monitors and televisions, consisting of a vacuum tube with an electron gun that emits beams of electrons onto a phosphorescent screen, producing images
- Daisy-Chaining - a method of connecting multiple devices in series, where each device is connected to the next one in line, typically used for connecting peripherals or external storage devices
- DDR (Double Data Rate) - a type of computer memory technology that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data transfer rate compared to single data rate (SDR) memory
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - a network protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other network configuration settings to devices on a local area network (LAN)
- DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) - a type of memory module used in computers, containing one or more memory integrated circuits and connecting to the motherboard via pins on both sides of the module
- DisplayPort Interface - a digital display interface used to connect monitors, TVs, and other display devices to computers, capable of transmitting high-resolution video and audio signals
- DNS (Domain Name System) - a hierarchical naming system for translating domain names (e.g., example.com) into IP addresses, enabling users to access websites and other network resources using human-readable names
- Down-Plugging - the act of inserting a connector or plug into a port in a downward direction, typically used to describe the orientation of connectors and ports for compatibility purposes
- DP++ (DisplayPort++) - a feature of DisplayPort interfaces that allows them to output HDMI or DVI signals using passive adapters, enabling compatibility with devices that use HDMI or DVI connections
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface) - a digital display interface used to transmit video signals between computers and display devices, supporting high-resolution digital video with various connector types, including DVI-I, DVI-D, and DVI-A
- Edge Contacts - electrical contacts located along the edge of a connector or electronic component, typically used for establishing electrical connections with corresponding contacts on another device or circuit board
- EIDE (Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics) - a standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard drives and optical drives, to a computer's motherboard, offering improved performance and features compared to the original IDE standard
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) - the disruption of electromagnetic signals caused by electromagnetic radiation emitted by electronic devices, cables, or other sources, leading to potential interference with the operation of nearby electronic equipment
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) - the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by contact or proximity, often resulting in damage to electronic components, particularly sensitive integrated circuits
- eSATA (External SATA) - an external interface for connecting SATA hard drives and other storage devices to a computer, providing faster data transfer rates and hot-swapping capabilities compared to USB or FireWire connections
- eSATAp (External SATA Power) - an external interface that combines eSATA and power connectors into a single cable, allowing for both data transfer and power delivery to compatible devices, such as external hard drives
- Expansion Card Slots - slots on the motherboard or expansion card riser where expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters, can be inserted to add additional functionality to a computer system
- Firewall - a network security device or software application that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, protecting a network from unauthorized access and malicious activities
- Front I/O Panel - the portion of a computer case's front panel that includes input/output ports for connecting peripherals and devices, such as USB ports, audio jacks, and card readers
- Front Panel - the part of a computer case or device that contains various input/output ports, buttons, and indicators, typically located on the front-facing side for easy access
- Full-duplex - a communication mode allowing simultaneous two-way data transmission, enabling both sending and receiving data at the same time
- GB/s (Gigabytes Per Second) - a unit of data transfer rate representing the number of gigabytes transferred per second, commonly used to measure the speed of data transfer in storage devices and network connections
- Gigahertz (GHz) - a unit of frequency equal to one billion cycles per second, typically used to measure the clock speed of computer processors
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) Architecture - understanding different GPU architectures (e.g., NVIDIA CUDA, AMD RDNA) and their features can be beneficial for studying graphics rendering, parallel processing, and GPU computing
- Graphics Memory - dedicated memory on a graphics card used to store graphical data and textures for rendering images and videos on a display
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) - a specialized processor designed to accelerate the rendering of images and videos, commonly used in graphics cards for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive tasks
- GT/s (Gigatransfers Per Second) - a unit of data transfer rate representing the number of billions of transfers per second, often used to measure the speed of data transfer in computer interconnects
- Half-duplex - a communication mode allowing data transmission in both directions, but not simultaneously, requiring alternating transmission and reception
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) - a data storage device that uses spinning magnetic disks to store and retrieve digital information, commonly used for long-term storage in computers and other electronic devices
- Hardware Port - interface on a computer or electronic device that allows for the connection of external peripherals or devices and facilitates the transfer of data, power, or audio/video signals between the device and peripherals
- HBA (Host Bus Adapter) - a hardware component that connects a computer or server to a storage device or network, facilitating data transfer between the host system and external storage devices
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) - a digital interface for transmitting high-definition audio and video signals between devices, commonly used to connect displays, TVs, and multimedia devices
- HDMI Port - interface used for transmitting high-definition audio and video signals between devices, such as computers, monitors, televisions, and video game consoles and support high-resolution digital video and multi-channel audio
- Headers - connectors or terminals on a motherboard or other electronic device used for connecting cables, providing input/output interfaces for various components such as USB, audio, and front-panel controls
- Heat Sink - a passive cooling device designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components, such as processors or graphics cards, to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance
- IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) - an interface standard for connecting storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives to a computer's motherboard
- ITX (Information Technology Extended) - a form factor specification for small-sized computer motherboards, typically used in compact desktops and media center systems
- Keying - a mechanism used in connectors or interfaces to ensure proper alignment and prevent incorrect insertion of plugs or cables by matching specific shapes, notches, or orientations
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) - a flat-panel display technology that uses liquid crystals to produce images, commonly used in computer monitors, TVs, and mobile devices
- LCD/TFT (Liquid Crystal Display Thin Film Transistor) - a type of LCD display that uses thin-film transistor technology to improve image quality and response time
- LED (Light-Emitting Diodes) - semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them, commonly used in electronic devices for indicators, displays, and lighting
- Lightning - a high-speed data transfer interface developed by Apple, commonly used for connecting iOS devices to computers for syncing and charging
- M.2 Interface - a small form factor interface for connecting solid-state drives (SSDs) and other expansion cards to a computer's motherboard, offering high-speed data transfer rates
- Mass Storage Device - a device used to store large amounts of data permanently or semi-permanently, such as hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and optical discs
- MB/s (Megabytes Per Second) - a unit of data transfer rate representing the number of megabytes transferred per second, commonly used to measure the speed of data transfer in storage devices and network connections
- Megahertz (MHz) - a unit of frequency equal to one million cycles per second, often used to measure the clock speed of computer processors and memory
- Micro-ATX / mATX (Micro Advanced Technology Extended) - a form factor specification for smaller-sized computer motherboards, offering a balance between compactness and expandability
- Mini-ITX (Mini Information Technology Extended) - a small form factor specification for computer motherboards, commonly used in compact desktops and home theater PCs
- MiniDP/mDP - a digital display interface used to connect monitors, projectors, and other display devices to computers, offering high-resolution video and audio transmission
- Molex - a type of electrical connector commonly used in computer power supplies and peripherals to provide power to components such as drives and fans
- Molex KK - a specific series of Molex connectors known for their reliability and versatility, often used in computer and electronic applications
- Motherboard - the main circuit board in a computer that houses the CPU, memory, expansion slots, and other essential components, providing connectivity and support for the system
- NIC (Network Interface Card) - a hardware component that enables a computer to connect to a network, facilitating communication with other devices and access to network resources
- Non-Volatile Device - a storage device or memory technology that retains data even when power is removed, ensuring data persistence and durability
- OLED (Organic LED) - a display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied, offering high contrast ratios and energy efficiency, commonly used in TVs, smartphones, and wearable devices
- Optical Disc Drive - a hardware component used for reading and writing data from optical discs, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs
- P1 Power Connector - a power connector typically found on computer motherboards, providing power to the CPU and other components
- PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) - an older interface standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard disk drives and optical drives, to a computer's motherboard using parallel data transfer
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) - a standard for connecting expansion cards to a computer's motherboard, providing high-speed data transfer between the CPU and peripheral devices
- PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) - a high-speed expansion bus standard for connecting peripheral devices to a computer's motherboard, offering faster data transfer rates than traditional PCI
- Peripheral Cable - a cable used to connect peripheral devices, such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices, to a computer, and transmitting data and power between the computer and the peripheral device
- Peripheral Device - an external device connected to a computer that extends its functionality or provides additional input/output capabilities, such as printers, scanners, keyboards, and external storage devices
- Power Supply Unit (PSU) - a device that converts AC power from a wall outlet into DC power suitable for use by a computer's internal components, while providing electrical power to the motherboard, drives, and other hardware components
- PS/2 - a type of port used to connect keyboards and mice to a computer, named after the Personal System/2 series of IBM computers that popularized it
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) - a data storage technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for redundancy, performance improvement, or both
- RAM (Random Access Memory) - a type of computer memory that allows data to be accessed randomly, providing fast read and write speeds for temporary storage of data and program instructions
- Raw Transfer Rate - the maximum data transfer rate of a storage device or interface before accounting for protocol overhead or encoding efficiency
- Rear Panel - the backside of a computer case or device where various ports, connectors, and expansion slots are located, allowing for connectivity with external devices and expansion cards
- RJ-45 Network/Ethernet Port - interface used for networking purposes, typically for connecting a computer or other device to a local area network (LAN) or the internet via Ethernet cables
- SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) - a high-speed interface standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard drives and tape drives, to a computer's motherboard, offering faster data transfer rates than traditional SCSI
- Molex - a type of electrical connector commonly used in computer power supplies and peripherals to provide power to components such as drives and fans
- Molex KK - a specific series of Molex connectors known for their reliability and versatility, often used in computer and electronic applications
- Motherboard - the main circuit board in a computer that houses the CPU, memory, expansion slots, and other essential components, providing connectivity and support for the system
- NIC (Network Interface Card) - a hardware component that enables a computer to connect to a network, facilitating communication with other devices and access to network resources
- Non-Volatile Device - a storage device or memory technology that retains data even when power is removed, ensuring data persistence and durability
- OLED (Organic LED) - a display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied, offering high contrast ratios and energy efficiency, commonly used in TVs, smartphones, and wearable devices
- Optical Disc Drive - a hardware component used for reading and writing data from optical discs, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs
- P1 Power Connector - a power connector typically found on computer motherboards, providing power to the CPU and other components
- PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) - an older interface standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard disk drives and optical drives, to a computer's motherboard using parallel data transfer
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) - a standard for connecting expansion cards to a computer's motherboard, providing high-speed data transfer between the CPU and peripheral devices
- PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) - a high-speed expansion bus standard for connecting peripheral devices to a computer's motherboard, offering faster data transfer rates than traditional PCI
- Peripheral Cable - a cable used to connect peripheral devices, such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices, to a computer, and transmitting data and power between the computer and the peripheral device
- Peripheral Device - an external device connected to a computer that extends its functionality or provides additional input/output capabilities, such as printers, scanners, keyboards, and external storage devices
- Power Supply Unit (PSU) - a device that converts AC power from a wall outlet into DC power suitable for use by a computer's internal components, while providing electrical power to the motherboard, drives, and other hardware components
- PS/2 - a type of port used to connect keyboards and mice to a computer, named after the Personal System/2 series of IBM computers that popularized it
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) - a data storage technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit for redundancy, performance improvement, or both
- RAM (Random Access Memory) - a type of computer memory that allows data to be accessed randomly, providing fast read and write speeds for temporary storage of data and program instructions
- Raw Transfer Rate - the maximum data transfer rate of a storage device or interface before accounting for protocol overhead or encoding efficiency
- Rear Panel - the backside of a computer case or device where various ports, connectors, and expansion slots are located, allowing for connectivity with external devices and expansion cards
- RJ-45 Network/Ethernet Port - interface used for networking purposes, typically for connecting a computer or other device to a local area network (LAN) or the internet via Ethernet cables
- SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) - a high-speed interface standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard drives and tape drives, to a computer's motherboard, offering faster data transfer rates than traditional SCSI
- SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) - a popular interface standard for connecting storage devices, such as hard disk drives and solid-state drives, to a computer's motherboard, offering high-speed serial data transfer
- SCA (Single Connector Attachment) - a type of hot-swappable SCSI connector used to connect SCSI hard drives to a server or storage device
- SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) - a set of standards for connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices, commonly used for connecting hard drives, tape drives, and scanners
- Serial Port - a type of communication interface used to transfer data serially, one bit at a time, between computers and peripheral devices, commonly used for connecting modems, printers, and serial mice
- Small Form Factor (SFF) - a design standard for compact computer components or systems, often used in small desktop computers or embedded systems
- Solid State Drive (SSD) - a storage device that uses flash memory to store data, providing faster data access and improved durability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs)
- Sound Card - a hardware device that processes audio signals from a computer's motherboard, converting digital audio into analog signals for output to speakers or headphones
- Standoffs - small metal or plastic spacers used to mount and support a motherboard inside a computer case, preventing electrical shorts and providing stability
- System Clock - a circuitry component that generates timing signals to synchronize the operations of a computer's components, including the CPU, memory, and peripherals
- Thermal Paste - a heat-conductive compound applied between a CPU or GPU and its heatsink to improve thermal conductivity and heat dissipation
- Throughput - the rate at which data is successfully transmitted or processed through a system, typically measured in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second (Bps)
- Thunderbolt - a high-speed input/output interface developed by Intel and Apple, capable of transferring data, video, and power over a single cable
- Tower Case - a type of computer case characterized by its tall, vertical design, typically housing the motherboard, drives, and other components
- Transistor - an electronic component used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power, forming the building blocks of modern electronic devices
- TRS (Tip, Ring, Sleeve) - a type of audio connector with three conductive areas, typically used for analog audio signals, supporting stereo or balanced connections
- Up-Plugging - connecting a cable or connector in a way that goes against the device's or port's orientation, ensuring proper connectivity
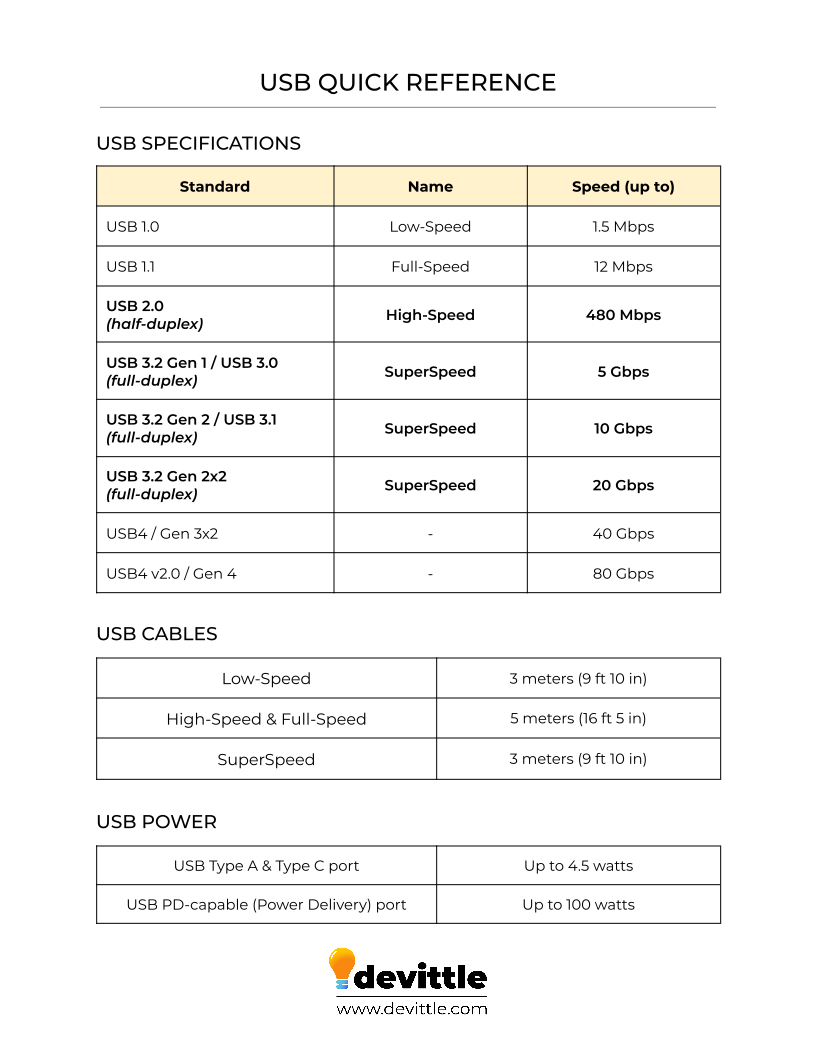
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) - a widely used interface standard for connecting peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage devices, to computers and other devices
- USB 2.0 - an earlier version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard, offering data transfer speeds of up to 480 megabits per second (Mbps)
- USB 3.0 - an updated version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard, offering faster data transfer speeds and improved power management compared to USB 2.0
- VGA (Video Graphics Array) - a video display standard used for connecting monitors and other display devices to computers, offering analog video signals
- Video Card - a hardware component responsible for generating and outputting visual information to a display device, commonly used in desktop computers for gaming and multimedia applications
- Volatile Device - a storage device or memory technology that loses its stored data when power is removed, requiring constant power to retain data
- Wi-Fi Adapter - a hardware device that enables a computer or other device to connect to a wireless local area network (Wi-Fi), providing wireless internet access and communication capabilities
- 2.4 GHz Frequency Band - A frequency band used for wireless communication in Wi-Fi networks, providing wider coverage but potentially slower speeds due to greater susceptibility to interference.
- 5 GHz Frequency Band - A frequency band used for wireless communication in Wi-Fi networks, offering faster speeds and less interference compared to the 2.4 GHz band, but with shorter range.
- 802.11a - A wireless networking standard that operates in the 5 GHz frequency band, offering data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) - A wireless networking standard that operates in the 5 GHz frequency band, providing faster data rates up to 867 Mbps per stream, and supports 8 x DL MU-MIMO.
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) - A wireless networking standard that improves upon previous standards by increasing efficiency, capacity, and performance in high-density environments by supporting 8 x DL and UL MU-MIMO, operating in both the 2.4 GHz and 5.4 GHz frequency bands, and data rates up to 1201 Mbps per stream.
- 802.11b - A wireless networking standard operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offering data rates up to 11 Mbps.
- 802.11g - A wireless networking standard operating in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, offering data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) - A wireless networking standard operating in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, offering data transfer rates up to 150 Mbps per stream, and 4 x MIMO.
- 8P8C Connector - Commonly known as an RJ-45 connector, it is used to terminate twisted pair cables in Ethernet networks.
- Access Point (AP) - A networking device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network, acting as a central hub for communication.
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) - A network protocol used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, enabling devices to communicate on a local network by resolving the hardware address of a device based on its IP address.
- Attenuation - The loss of signal strength as it travels through a medium, such as a cable or fiber optic, resulting in weaker signals over distance.
- Bandwidth - The maximum data transfer rate of a network or internet connection, typically measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Biometric Authentication - A security measure that uses unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to verify a user's identity.
- Blocklisting - A security technique used to prevent access to specific websites, IP addresses, or services deemed harmful or undesirable.
- Bluetooth - A wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances between devices, commonly used for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and headphones.
- Cable Tester - A tool used to verify the integrity and connectivity of network cables by testing for continuity, shorts, and miswires.
- Cat 5 Cable - A type of twisted pair cable commonly used in Ethernet networks, supporting data rates up to 100 Mbps.
- Cat 5e Cable - An enhanced version of Cat 5 cable with improved performance and reduced crosstalk, supporting data rates up to 1 Gbps.
- Cat 6 Cable - A type of twisted pair cable designed for high-speed Ethernet networks, supporting data rates up to 10 Gbps.
- Cat 6a Cable - An augmented version of Cat 6 cable with improved performance and bandwidth, supporting data rates up to 10 Gbps over longer distances.
- Channels - Frequencies within the designated frequency bands used for wireless communication, allowing multiple devices to operate simultaneously without interference.
- Client - A device or software application that requests services or resources from a server on a network.
- Cloud Computing - The delivery of computing services over the internet, including storage, processing power, and software, allowing users to access resources remotely on demand.
- Coaxial Cable - A type of cable consisting of a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and a metallic shield, commonly used for cable television and broadband internet connections.
- Computer Networking - The practice of connecting computers and other devices to share resources and communicate with each other, enabling data exchange and collaboration.
- Data Center - A facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as servers, storage systems, and networking equipment, for storing, processing, and distributing data.
- Domain Name System (DNS) - A hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the internet or a private network, translating.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) - A network management protocol that dynamically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network, simplifying network administration and reducing configuration errors.
- Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) - A mechanism used in Wi-Fi networks to dynamically select and switch channels to avoid interference from radar systems operating in the same frequency band.
- Encryption - The process of converting data into a form that is unreadable to unauthorized users, typically done to protect sensitive information during transmission or storage.
- F-Type Connector - A coaxial connector used for terminating coaxial cables, commonly found in cable television and satellite television installations.
- Fiber Optic Cable - A high-speed transmission medium consisting of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that transmit data using light signals, offering advantages such as high bandwidth, low latency, and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
- Firewall - A network security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, protecting against unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Frequency Band - A range of frequencies allocated for wireless communication, such as the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands used in Wi-Fi networks.
- Gateway - A networking device or software that serves as an entry point between different networks, facilitating communication and translation between different protocols or network architectures.
- Host - A computer or device on a network that sends or receives data, typically identified by an IP address.
- Hub - A networking device that connects multiple devices in a network, allowing them to communicate with each other by forwarding data to all connected devices.
- IEEE 802.11 Standard - A set of standards developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for wireless LANs, specifying protocols for communication between devices in Wi-Fi networks.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - A cloud computing model where virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, are provided over the internet as a service.
- Infrastructure Mode - A mode of operation for wireless networks where devices communicate through an access point, enabling connectivity to a wired network and internet access.
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) - The organization responsible for overseeing the global coordination of IP address allocation, domain name system management, and protocol parameter assignment.
- Internet of Things (IoT) - The network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data, automate tasks, and communicate with each other.
- IP Address - A numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication, identifying its location in the network.
- IPv4 Address - A 32-bit numerical address used to identify devices on a network using the Internet Protocol version 4, expressed as four decimal numbers separated by periods.
- IPv6 Address - A 128-bit numerical address used to identify devices on a network using the Internet Protocol version 6, designed to address the limitations of IPv4 and accommodate the growing number of internet-connected devices.
- Latency - The time delay between the sending and receiving of data packets in a network, often measured in milliseconds (ms), influencing the responsiveness and performance of networked applications and services.
- Linux - A popular open-source operating system kernel used in a wide range of computing devices, including servers, desktops, and embedded systems.
- Local Area Network (LAN) - A network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or campus, allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other directly.
- Load Balancer - A networking device or software that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources to ensure high availability, reliability, and scalability of applications and services.
- Local Area Network (LAN) - A network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or campus, allowing them to share resources and communicate with each other directly.
- Loopback Plug - A connector used to test network interfaces by looping transmitted signals back to the source for verification.
- Lucent Connector (LC) - A fiber optic connector commonly used in networking equipment and fiber optic cabling, featuring a small form factor and high performance.
- MAC Address (Media Access Control Address) - A unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment, typically represented as a series of hexadecimal digits.
- Managed Switch - A networking switch with advanced features and capabilities, such as VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS) management, and port mirroring, configurable through a management interface.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) - A network that spans a geographic area larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, connecting multiple buildings or sites within a city or metropolitan area.
- MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) - A technology used in wireless communication systems to improve performance and throughput by transmitting and receiving multiple data streams simultaneously using multiple antennas.
- Modem - A device that modulates and demodulates analog signals to encode and decode digital information for transmission over telephone lines, cable systems, or wireless networks, enabling internet connectivity for computers and other devices.
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output) - An extension of MIMO technology that enables a wireless access point to communicate with multiple clients simultaneously, increasing network efficiency and capacity.
- Near-field Communication (NFC) - A short-range wireless communication technology that enables devices to exchange data when they are brought into close proximity, commonly used for contactless payments and data transfer.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) - A technique used in routers or firewalls to modify network address information in data packet headers while in transit, enabling multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address for internet access.
- Network Administrator - A professional responsible for managing and maintaining computer networks, including tasks such as installation, configuration, troubleshooting, and security management.
- Network Interface Card (NIC) - A hardware component that enables a computer or device to connect to a network, providing a physical interface for transmitting and receiving data.
- Network Segmentation - The practice of dividing a computer network into smaller subnetworks to improve performance, security, and manageability by controlling the flow of traffic between segments.
- Next-generation Firewalls (NGFWs) - Advanced network security appliances that incorporate traditional firewall features with additional capabilities, such as intrusion detection and prevention, application awareness, and advanced threat protection.
- Operating System - Software that manages computer hardware and provides services for computer programs, including tasks such as memory management, process scheduling, and user interface.
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) - A technology used in Wi-Fi 6 networks to improve efficiency and capacity by dividing the available spectrum into smaller subchannels and allowing multiple devices to transmit data simultaneously.
- Packet - A unit of data transmitted over a network, consisting of a header containing control information and a payload containing the actual data being transmitted.
- Passive Optical Network (PON) - A telecommunications technology that uses fiber-optic cables to deliver data, voice, and video services to subscribers without the need for active electronics in the network.
- Patch Panel - A panel with multiple ports used to organize and manage network connections, typically used to terminate and interconnect twisted pair cables in a structured cabling system.
- Personal Area Network (PAN) - A network that spans a small area, typically within the range of an individual's personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) - A cloud computing model where a provider delivers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
- Plenum - A type of cable jacketing material that meets fire safety and smoke emission standards, commonly used in air handling spaces such as plenum ceilings.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) - A technology that allows electrical power to be transmitted over Ethernet cables along with data, enabling devices such as IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones to be powered over the same cable used for network connectivity.
- Powered Device (PD) - A device that receives power from a Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch or injector, such as IP phones, wireless access points, and network cameras.
- Power Injector - A device used to inject electrical power into Ethernet cables for powering Powered Devices (PDs) in Power over Ethernet (PoE) networks.
- Proxy Server - An intermediary server that acts as a gateway between a user's device and the internet, intercepting requests and forwarding them on behalf of the user, often used for security, privacy, and performance optimization.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) - A technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, commonly used for inventory management, access control, and contactless payment systems.
- RJ-45 Connector - A type of connector commonly used for Ethernet connections, featuring eight pins and used with twisted pair cables terminated with 8P8C connectors.
- Router - A networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks, typically using routing tables to determine the best path for transmission.
- Server - A computer or software application that provides services or resources to other computers or devices on a network, such as file storage, email, web hosting, and database management.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) - A type of twisted pair cable that includes additional shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, commonly used in environments with high levels of electrical noise.
- Small Office Home Office (SOHO) - A term used to describe a small-scale business or home-based office setup, typically with fewer than 10 employees and minimal IT infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) - A cloud computing model where software applications are hosted by a provider and made available to customers over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance on local devices.
- Storage Area Network (SAN) - A specialized high-speed network that provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage, allowing multiple servers to access shared storage devices such as disk arrays and tape libraries.
- Subscriber Connect (SC) - A type of fiber optic connector commonly used in telecommunications and networking equipment, featuring a push-pull coupling mechanism for easy connection and disconnection.
- Subnet Mask - A numeric identifier used in IPv4 addressing to divide an IP address into network and host portions, determining the network's size and allowing for efficient routing.
- Switch - A networking device that connects devices within a local area network (LAN) and forwards data packets to their intended destination based on MAC addresses.
- Systems Administrator - A professional responsible for managing and maintaining the hardware, software, and networks within an organization, including tasks such as installation, configuration, troubleshooting, and security management.
- T568A/T568B - Two wiring schemes used for terminating Ethernet cables with RJ-45 connectors, specifying the arrangement of wire pairs and pin assignments for compatibility with different networking standards.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) - A connection-oriented protocol used in the internet protocol suite for reliable and ordered delivery of data packets between devices on a network.
- Threat Detection - The process of identifying and analyzing potential security threats or breaches within a computer network, enabling proactive responses to mitigate risks and protect assets.
- TIA/EIA Standard - Standards developed by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) to define specifications and requirements for telecommunications and networking equipment and cabling.
- Tone Generator - A tool used in network testing and troubleshooting to generate an audio tone that can be traced along a cable, helping to identify and locate cable runs and faults.
- Troubleshooting - The systematic process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems within a computer system or network to restore functionality and prevent future issues.
- Unmanaged Switch - A networking switch with basic functionality and no configuration options, allowing devices to connect and communicate with each other without the need for manual setup or management.
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) - A type of twisted pair cable commonly used in Ethernet networks, consisting of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), without additional shielding.
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP) - A connectionless protocol used in the internet protocol suite for fast and lightweight transmission of data packets between devices on a network, often used for real-time communication and multimedia streaming.
- Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) - A logical grouping of devices within a LAN, allowing for segmentation and isolation of network traffic based on criteria such as department, function, or security requirements.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) - A secure network connection that allows users to access and transmit data over a public network, such as the internet, as if they were directly connected to a private network, ensuring privacy and security.
- Virtualization - The technology that enables the creation of virtual versions of computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networks, allowing multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical machine.
- Wide Area Network (WAN) - A network that spans a large geographical area, connecting multiple local area networks (LANs) and other types of networks to enable long-distance communication and data exchange.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) - A type of local area network that uses wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, to connect devices within a limited geographical area, typically using access points to provide connectivity.
- Accelerometer - A sensor that detects the orientation and movement of a device, such as tilting or rotating, and adjusts the display or interface accordingly.
- App Store - An online marketplace or platform where users can browse, download, and install applications (apps) for their mobile devices, typically curated and maintained by the device's operating system provider.
- Battery Life - The duration for which a mobile device can operate on a single battery charge, influenced by factors such as usage patterns, screen brightness, and background processes.
- Biometric Authentication - A security measure that uses unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to verify a user's identity and grant access to the device or its features.
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) - A policy or practice allowing employees to use their personal mobile devices for work-related tasks, often requiring security measures such as device encryption, remote wipe, and containerization to protect sensitive data.
- Digitizer - A component or layer in a touchscreen device that converts analog touch input into digital signals, enabling the device to accurately detect and respond to touch interactions.
- GPS (Global Positioning System) - A satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information to GPS-enabled devices, allowing users to determine their precise geographic coordinates and navigate routes.
- Gyroscope - A sensor that measures angular velocity and rotation, providing information about the device's orientation and movement, often used in conjunction with accelerometers for enhanced motion sensing.
- IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) - A unique 15-digit code assigned to every mobile device by its manufacturer, used to identify the device on cellular networks and blacklist stolen or lost devices.
- Jailbreaking (iOS) / Rooting (Android) - The process of removing software restrictions imposed by the device manufacturer or operating system provider to gain elevated privileges and access to the device's file system and settings, allowing users to install unauthorized apps and modify system behavior.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) - A type of flat-panel display technology used in mobile devices, consisting of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of glass and controlled by electric currents to produce images.
- MicroSD Card - A type of removable flash memory card used for storage expansion in mobile devices, providing additional space for apps, photos, videos, and other data.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM) - A system or software solution used by organizations to monitor, manage, and secure mobile devices deployed within their network, including configuration, application deployment, and device tracking.
- Mobile Device Repair - The process of troubleshooting, diagnosing, and repairing hardware and software issues on mobile devices, including tasks such as screen replacement, battery replacement, and software troubleshooting.
- Mobile Device Security - The protection of mobile devices and the data they contain from unauthorized access, theft, loss, malware, and other security threats, implemented through measures such as encryption, biometric authentication, and remote wipe.
- Mobile Hotspot - A feature on mobile devices that allows them to function as wireless access points, enabling other devices to connect to the internet using the device's cellular data connection.
- Mobile Operating System - The software platform that manages the operations and functions of mobile devices, including user interfaces, application management, and hardware interaction, examples include Android, iOS, and Windows Mobile.
- Near Field Communication (NFC) - A short-range wireless communication technology that enables devices to establish communication by bringing them into close proximity, often used for contactless payments, access control, and data transfer.
- OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) - A display technology used in mobile devices that emits light when an electric current passes through organic compounds, offering brighter colors, higher contrast, and better energy efficiency compared to LCD screens.
- Push Notifications - Messages or alerts sent from applications or services to a user's mobile device, typically displayed as notifications on the device's screen, providing updates, reminders, or important information.
- SIM Card (Subscriber Identity Module) - A small removable card containing a subscriber's information used to authenticate and identify the user on a mobile network, allowing access to voice, data, and other services.
- SODIMM (Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module) - A type of memory module commonly used in laptops and other small form factor computers, offering a compact design suitable for constrained spaces.
- Touchscreen - A display screen that responds to touch input, allowing users to interact with the device by tapping, swiping, pinching, or other gestures.
- USB-C - A reversible and versatile USB connector standard commonly used in modern mobile devices, offering faster data transfer speeds, higher power delivery, and compatibility with various peripherals.
- Wireless Charging - A technology that enables charging of mobile devices without the need for physical cables, typically using electromagnetic induction or resonance to transfer power.
- Calibration - The process of adjusting printer settings or components to ensure accurate color reproduction, print alignment, and overall print quality.
- Dot Matrix Printer - A type of impact printer that forms characters and images by striking pins against an ink-soaked ribbon to create dots on paper.
- Driver - Software that allows a computer to communicate with and control a printer, translating print commands from applications into printer-specific language and settings.
- Duplex Printing - The capability of a printer to automatically print on both sides of a sheet of paper, reducing paper usage and manual intervention.
- Error Codes - Numeric or alphanumeric codes displayed by the printer to indicate specific issues or malfunctions, helping users diagnose and troubleshoot problems.
- Ghosting - A printing defect characterized by faint or faded copies of printed images or text, often caused by issues with the imaging drum or toner cartridge.
- Inkjet Printer - A type of printer that sprays tiny droplets of liquid ink onto paper to create images or text.
- Laser Printer - A type of printer that uses a laser beam to produce images on a photosensitive drum, which is then transferred to paper and fused with heat.
- Maintenance Kit - A collection of replacement parts and consumables, such as rollers and fusers, used to maintain and repair printers.
- Misalignment - A printing defect where printed text or images appear skewed or out of position on the page, often caused by improper paper loading or alignment issues with print heads or toner cartridges.
- Multifunction Printer (MFP) - A printer that combines the functions of printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing into a single device.
- Network Printer - A printer that is connected to a network and can be accessed and shared by multiple users over the network, typically using Ethernet or Wi-Fi connectivity.
- Paper Jam - A situation where paper becomes stuck in the printer's paper path, preventing normal printing operations and requiring manual intervention to clear.
- PCL (Printer Command Language) - Developed by Hewlett-Packard, PCL is a printer language used for controlling laser printers and inkjet printers. It provides basic commands for page layout, font selection, and graphics rendering, offering compatibility with a wide range of printers.
- PostScript - Developed by Adobe Systems, PostScript is a page description language used for printing documents containing text, images, and vector graphics. It is widely supported by printers and desktop publishing software, offering high-quality output and device independence.
- Print Head - The component of an inkjet printer that contains the nozzles used to spray ink onto the paper.
- Print Quality - The clarity, sharpness, and accuracy of printed output, affected by factors such as resolution, ink or toner quality, and paper type.
- Print Queue - A list of print jobs waiting to be processed by a printer, managed by the operating system or print server.
- Print Spooler - A software component in the operating system that manages print jobs, queuing and scheduling them for printing, and handling communication between applications and printers.
- Printer - A peripheral device that produces text or graphics on paper or other media.
- Printer Driver - Software that enables a computer to communicate with a printer, translating print commands into a format that the printer can understand.
- Printer Languages - Programming languages or protocols used by printers to interpret and process print jobs sent from computers or other devices.
- Printer Maintenance - Regular cleaning, inspection, and upkeep of printer components to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and print quality.
- Printhead Alignment - The process of adjusting the alignment of the printhead nozzles to ensure precise placement of ink or toner on the paper.
- Resolution - The level of detail and clarity in printed output, typically measured in dots per inch (DPI) for printers, indicating the number of individual dots that can be printed in a linear inch.
- Smudging - A printing defect characterized by blurred or streaked output caused by improper drying of ink or toner on the paper, leading to smudges or stains.
- Thermal Printer - A type of printer that uses heat to produce images or text on heat-sensitive paper, commonly used in receipt printers and label printers.
- Toner Cartridge - A replaceable component in laser printers containing toner powder used to create text and images on paper.
- Troubleshooting - The process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues with a printer, including hardware malfunctions, software errors, and print quality issues.
- Wireless Printing - The ability to send print jobs to a printer wirelessly from a computer or mobile device, using technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cloud printing services.